In humans and other vertebrates, the nervous system is comprised of two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
Cells of the nervous system
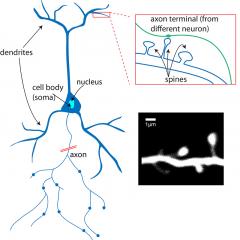
The brain and nervous system are made of nerve cells called neurons. Neurons send electrochemical signals to one another, forming the basis of the brain’s complex, essential functions: to form memories and thoughts, to produce actions, and to interpret the world around us. The brain contains around 100 billion neurons. But neurons don’t work alone. In fact, there are as many non-neuronal cells, called glia, in the brain as there are neurons, if not more.
Neurons
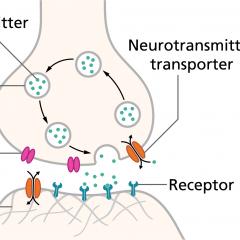
Action potentials and synapses
Glia
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) contains the brain and spinal cord, and forms the majority of the nervous system. The brain is protected by the thick bones of the skull, and the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae.
Brain
Spinal cord
Neuroplasticity
The brain is a remarkably adaptive organ. Neurons and the connections between them are continually changing, which allow us to acquire new skills, retain memories, and recover from brain injury. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain and nervous system’s ability to re-model in response to new information. Being plastic, the brain can change as a result of behaviour, emotions, external stimuli and injury.
One mechanism through which this occurs is synaptic plasticity, which occurs at synapses and is crucial for forming new memories. Another is the birth of new neurons, which is known as neurogenesis.
Synaptic plasticity
How do scientists study synaptic plasticity and learning?
Neurogenesis
Are new neurons formed in the adult brain?
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) connects the CNS to limbs and organs. The PNS is divided into the:
Autonomic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
Enteric nervous system