The best neuroscience images from QBI in 2017 have been announced.
QBI Choice Award Winner
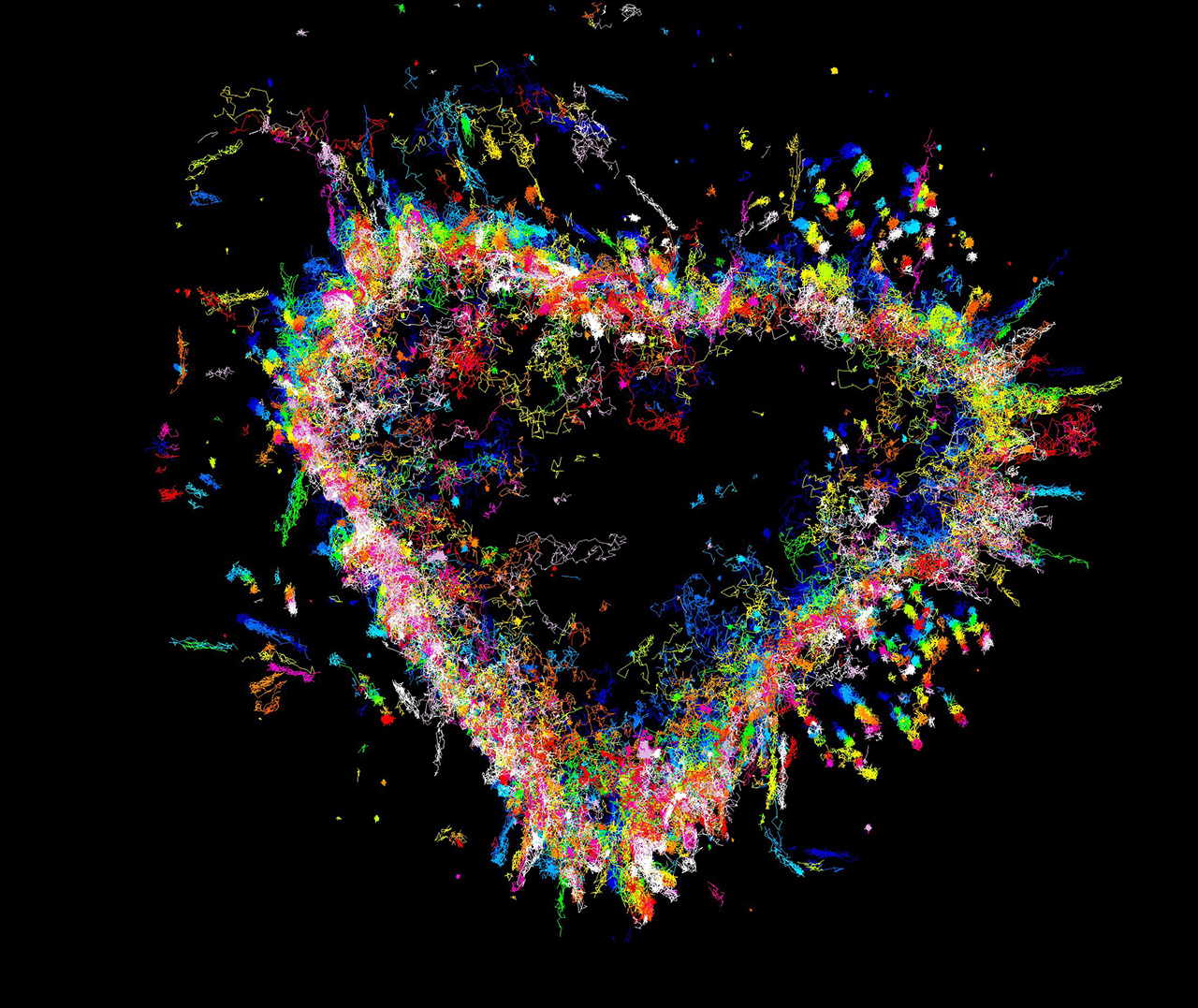

Ravikiran Kasula, PhD student, Meunier Lab
The trajectories of syntaxin-1a on the plasma membrane of Munc18-1/2 double knockout, DKO- (PC12) cells. We have used a technique called uPAINT to image transmembrane protein (syntaxin-1a tagged with an extracellular GFP) by adding fluorescent nanobodies that bind to GFP (AntiGFP-ATTO647N) to the imaging medium. We then used specialised software to create a super-resolved image of the trajectories of syntaxin 1a.
Public Choice Award Winner
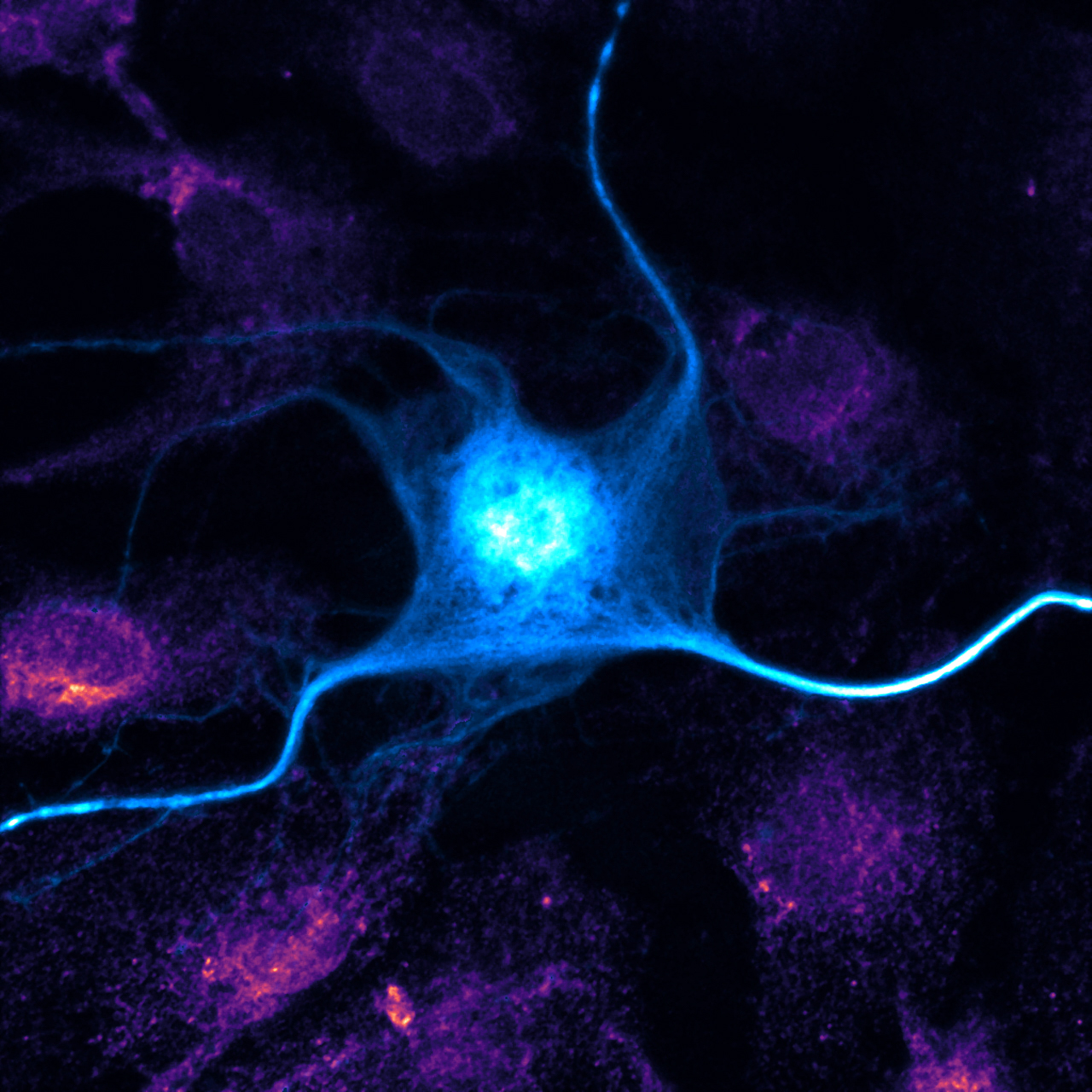
Amandine Grim, Postdoctoral research fellow, Götz lab
The blue neuron expresses a protein tagged with a fluorescent marker. The pink of surrounding cells is formed from endoplasmic reticulum, a cell structure that is important for protein processing and transport.
Technical Category Winner
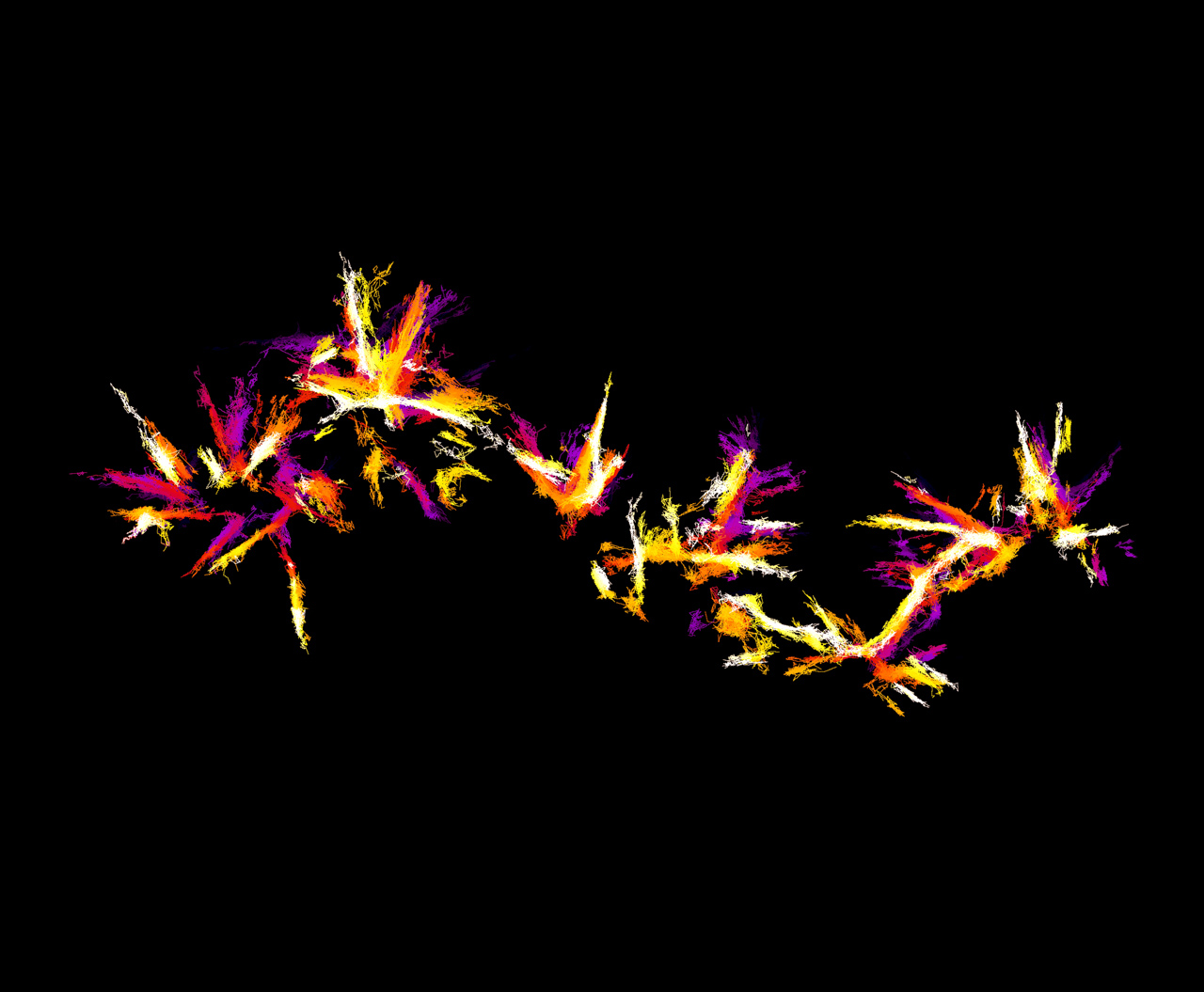
Merja Joensuu, Postdoctoral research fellow, Meunier lab
They may look like fireworks, but this image shows nanoscopic movements of single actin molecules. Actin is an essential protein found in all cells of plants and animals, in this case, a neurosecretory cell, a specialised type of nerve cell that releases message molecules into the blood.
Scientific Category Winner
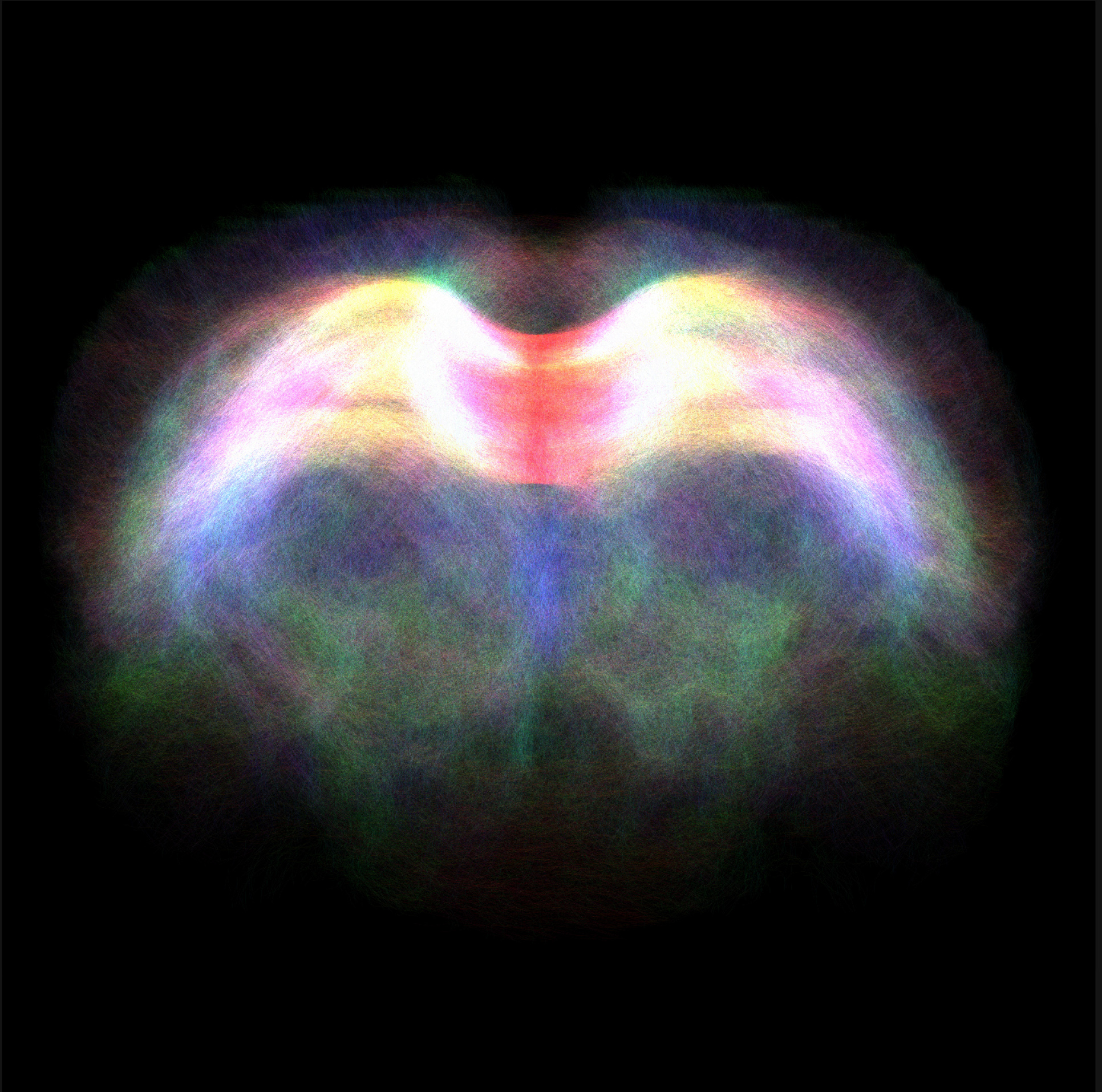
Abdalla Mohamed, PhD student, Nasrallah lab
Diffusion tensor imaging, an MRI-based neuroimaging technique, reveals the fibre tracts through the corpus callosum in a rodent brain. The corpus callosum links the brain's left and right hemispheres to each other.
Artistic Category Winner
Leon We Luan, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Eyles lab
A side view of a mouse embryonic brain. The dopamine axons (dark blue) grow towards their target brain regions.
Video Category Winner
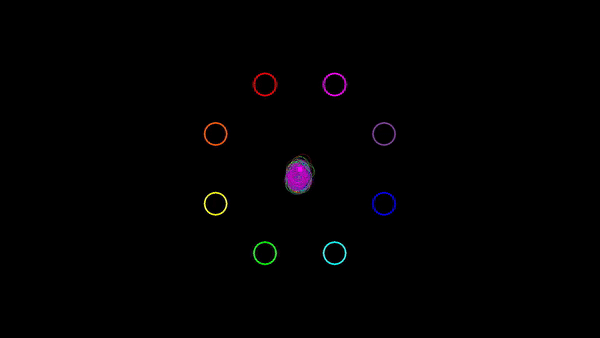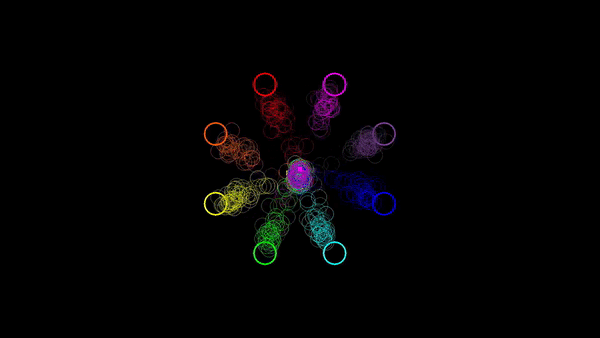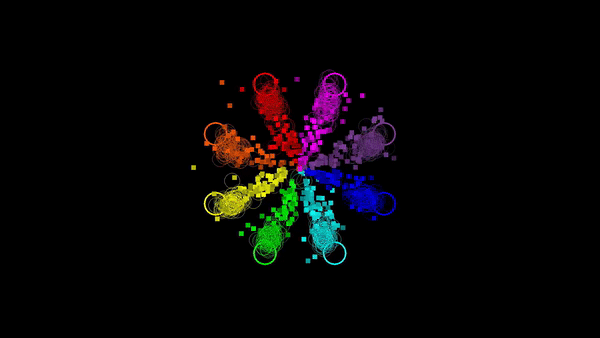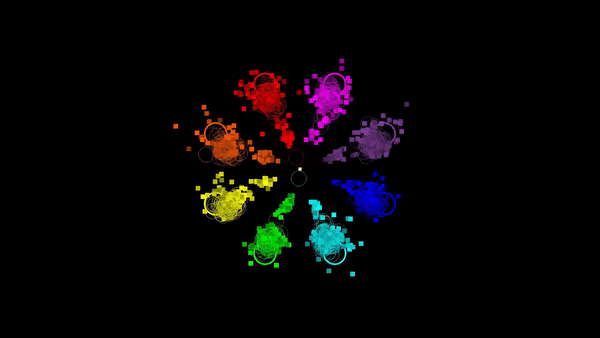
Angela Renton, PhD Student, Mattingley lab
The eye movements (coloured rings) and cursor movements (coloured squares) of pairs of participants using joysticks to move cursors towards eight cued locations on a display.



